Uncategorized
Art for the Asking: Check-Out Art From The Graphic Arts Loan Collection At The Morrison Library August 26 & 27
 The Graphic Arts Loan Collection (GALC) at the Morrison Library has been checking out art to UC Berkeley students, staff, and faculty since 1958 and it is back again this year!
The Graphic Arts Loan Collection (GALC) at the Morrison Library has been checking out art to UC Berkeley students, staff, and faculty since 1958 and it is back again this year!
 The purpose of the GALC since its inception has been to put art in the hands of UC Berkeley students (and the best way to appreciate art is to live with it!), so on August 26 and 27, from 10am to 4pm, UC Berkeley students can come to the Morrison Library (101 Doe Library) and check-out up to two pieces of art from the GALC’s collection to take home and hang on their walls for the academic year. The prints will be available to students on a first come, first served basis.
The purpose of the GALC since its inception has been to put art in the hands of UC Berkeley students (and the best way to appreciate art is to live with it!), so on August 26 and 27, from 10am to 4pm, UC Berkeley students can come to the Morrison Library (101 Doe Library) and check-out up to two pieces of art from the GALC’s collection to take home and hang on their walls for the academic year. The prints will be available to students on a first come, first served basis.
If you would like to see what we have before you come to the Morrison Library, all the prints are available to browse online at the Graphic Arts Loan Collection website. Not everything in the collection will be available at the Morrison Library these days, but much of the collection will. Please note that the Graphic Arts Loan Collection will not be available to staff and faculty members during this time, but only available to UC Berkeley students. Starting August 29th students can reserve prints from the collection through the GALC website, and on September 9th, faculty and staff can begin reserving prints. Any questions about the GALC can be directed to graphicarts-library@berkeley.edu.



Carrie Mae Weems, Untitled: Trees With Mattress Culebra en el Petate, Sergio Sanchez Santamaria Faith Ringgold, Jo Baker’s Birthday
Primary source: Environmental History: Conservation and Public Policy in America, 1870-1980
 The Library has gained access to the online archive “Environmental History: Conservation and Public Policy in America, 1870-1980” thanks to the Institute for Governmental Studies Library’s contribution of nearly 2,000 items to this collection.
The Library has gained access to the online archive “Environmental History: Conservation and Public Policy in America, 1870-1980” thanks to the Institute for Governmental Studies Library’s contribution of nearly 2,000 items to this collection.
A detailed description from the vendor’s website:
Starting in the late nineteenth century, in direct response to the Industrial Revolution, forces in social and political spheres struggled to balance the good of the public and the planet against the economic exploitation of resources. Environmental History: Conservation and Public Policy in America, 1870–1980 chronicles various responses in the United States to this struggle through key primary sources from individual activists, advocacy organizations, and government agencies.
Collections Included
- Papers preserved at Yale University of George Bird Grinnell, a founding member of the Boone and Crockett Club, one of the earliest American wildlands preservation organizations; a founder of the first Audubon Society and New York Zoological Society; and editor for 35 years of the outdoorsman magazine Forest and Stream, which played a key role as an early sponsor of the national park movement and Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918.
- Records housed at the Denver Public Library of the American Bison Society, an organization that sought to save the American bison from extinction and succeeded as the first American wildlife reintroduction program.
- Also housed at the Denver Public Library, the papers of key women conservationists, such as Rosalie Edge and Velma “Wild Horse Annie” Johnston. Edge formed the Emergency Conservation Committee to establish Hawk Mountain Sanctuary (the first preserve for birds of prey), clashed with the Audubon Society over its policy of protecting songbirds at the expense of predatory species, and was a leading advocate for establishing the Olympic and Kings Canyon national parks. Johnston worked to end the capture and killing of wild mustang horses and free-roaming donkeys and lobbied to protect all wild equine species.
- Documents held at various institutions of the “father of forestry” Joseph Trimble Rothrock, who served as the first president and founder of the Pennsylvania Forestry Association and Pennsylvania’s first forestry commissioner. Rothrock’s work acquiring land for state parks and forests illustrates the role of key actors at state and regional levels.
- Project histories and reports of the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation from the National Archives and Records Administration, chronicling the bureau’s work on projects including Belle Fourche, South Dakota; Grand Valley, Colorado; Klamath, Oregon; Lower Yellowstone, Montana; Shoshoni, Wyoming; and more.
- Select gray literature on conservation and environmental policy from the Institute of Governmental Studies Library at the University of California at Berkeley. This vast array of documents issued by state, regional, and municipal agencies; advocacy organizations; study groups; and commissions from the 1920s into the 1970s cover wildlife management, land use and preservation, public health, air and water quality, energy development, and sanitation.
Curating Literature @UC Berkeley’s Center for Latin American and Caribbean Studies
Curating Literature

This online event on curating literary festivals will feature: Milena Britto, curadora literaria independiente; Natalia Brizuela, curadora y editora independiente; Cristina Fuentes La Roche, Directora, Hay Festival; Mauro Munhoz, Co-fundador y Director FLIP, Festa Literária Internacional de Paraty; Jamille Pinheiro Dias, curadora independente; Amalia Sanz, Directora FILBA, Festival Internacional de Literatura de Buenos Aires.
This event will be in Spanish and Portuguese, with simultaneous interpretation into English
Arab-American Heritage Month 2024

Hey there, bookworms! Ready to celebrate Arab American Heritage Month with a literary twist? Join us as we dive into the captivating world of Arab-American authors and characters and their vibrant stories, both fiction and nonfiction. Explore more at UCB Overdrive today!
Kaveh Akbar
Etaf Rum
Aisha Abdel Gawad
Sarafina El-Badry Nance
Hanan al-Shaykh
Nazanine Hozar
Trial of Cine Cubano ending on March 29 2024
Cine Cubano is a journal that provides valuable insights into Cuban revolutionary cinema and Latin American cinema. It has over 200 issues from 1960 to 2019, covering six decades of film theory, techniques, and reviews. The journal has now been digitized and made available online for the first time, providing unprecedented access to film scholars and students. All 205 print issues have been scanned and included in this new online collection. The scanning was done at the ICAIC Film Institute in Havana, Cuba, where the journal originated. Overall, this is an important new digital resource for studying the history of Cuban and Latin American cinema. The online availability makes decades of film knowledge more accessible.
Women’s History Month 2024

Empowerment, inspiration, and a dash of magic: Celebrating Women’s History Month with a collection that bridges worlds, both real and imagined, penned by fierce women who redefine history, one page at a time! Check out UCB Overdrive for more great finds.
Mattie Kahn
Vanessa Chan
Safiyah Sinclair
Kristin Hannah
Parini Shroff
Margaret Verble
Jasmine Brown
Jenni Nuttall
Sandra Guzman
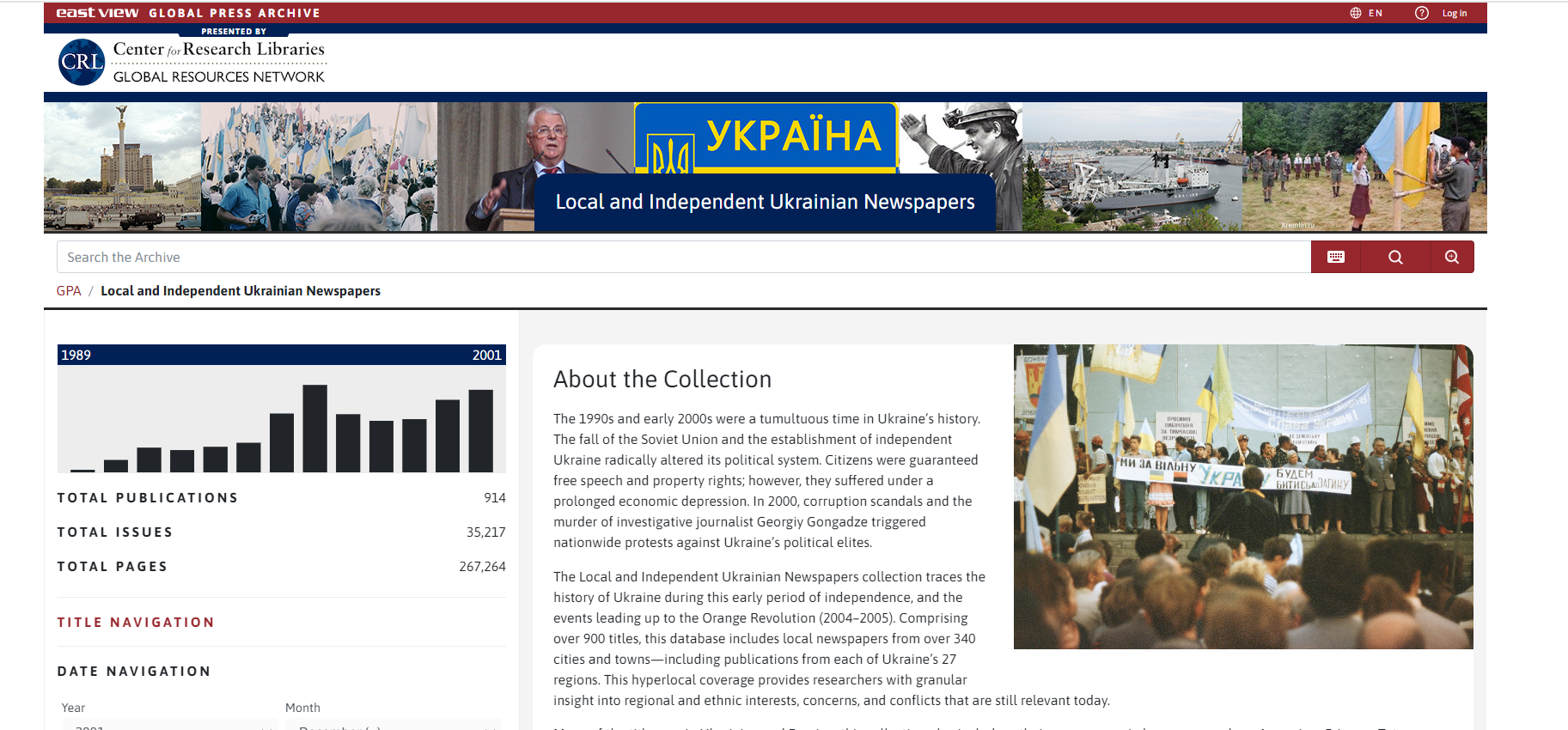
Local and Independent Ukrainian Newspapers on Global Press Archive Electronically Available
The 1990s and early 2000s marked a turbulent period in Ukraine’s history due to the fall of the Soviet Union and the emergence of an independent Ukraine. Despite gaining free speech and property rights, citizens faced economic hardships. Corruption scandals and the murder of journalist Georgiy Gongadze in 2000 sparked nationwide protests against the political elite. The Local and Independent Ukrainian Newspapers collection covers this era up to the Orange Revolution (2004–2005), offering insights from over 900 newspapers across 340 cities, reflecting regional and ethnic dynamics. The collection includes publications in Ukrainian, Russian, and other languages like Armenian, German, Polish, etc., providing a detailed view of historical events. Access to this database is supported by the Center for Research Libraries and its members.
One can access this collection here.
PhiloBiblon 2024 n. 2 (Fevereiro): Os anais portugueses (séculos XIV-XVI) e a BITAGAP
Filipe Alves Moreira
IF/Universidade do Porto e Universidade Aberta
Como já foi destacado em diversas ocasiões (p. ex., Sharrer 2022), o trabalho da equipa da BITAGAP em bibliotecas e arquivos portugueses e de outros países tem descoberto, (re)localizado e identificado uma grande quantidade de textos e manuscritos de que não havia conhecimento, permitindo assim alargar consideravelmente a base empírica de estudo da cultura galega e portuguesa da Idade Média. Por vezes, essas descobertas dizem respeito não apenas a um texto ou autor em específico, mas a um género textual. É o que sucede com os anais escritos, em língua portuguesa, entre finais do século XIV e inícios do século XVI.
Contrariamente aos anais portugueses escritos em latim durante o século XII e início do XIII, que contam já com diferentes edições e uma sólida investigação que lhes tem sido dedicada (p. ex.: David 1947, Bautista 2009, Furtado 2021), os anais portugueses escritos a partir do século XIV, e especialmente os que foram escritos em português (que são quase todos) estão inéditos ou muito insuficientemente estudados e editados. Existe, até, a ideia de que o género analístico é algo especificamente medieval. Nada mais falso, porém: pelo menos em Portugal, não só continuou a escrever-se anais ao longo dos séculos XVI-XVII, como, até, dir-se-ia que foram mais comuns nessa época, do que anteriormente.
É, todavia, compreensível que os anais em português dos séculos XIV, XV e inícios do XVI estejam ainda inéditos ou insuficientemente editados e não tenham sido estudados: é que a maior parte deles eram completamente desconhecidos, antes das sucessivas atualizações de BITAGAP, ao longo dos últimos dez anos. Foi a BITAGAP que, pela primeira vez, apresentou um corpus de anais escritos em português, muitos deles descobertos e identificados devido às investigações da equipa. Este corpus está facilmente acessível através de uma busca em Obra por “Anais medievais” em “Assunto”.
A mais recente atualização de BITAGAP contém um elenco de 21 destes anais. Como sempre acontece com este tipo de textos, não é fácil estabelecer-se uma cronologia para cada um deles. A maior parte subsiste, aparentemente, em cópias únicas, maioritariamente datáveis do século XVI, mas os acontecimentos históricos mais recentes neles mencionados variam entre finais do século XIV e inícios do século XVI. Quase todos concentram-se na história portuguesa, começando habitualmente, ou com a batalha do Salado (1340), ou com a guerra de Aljubarrota e a ascensão de D. João I ao trono (1385), eventos que assim adquirem estatuto fundacional. São especialmente numerosas as entradas relativas a acontecimentos dos reinados de D. Duarte, D. Afonso V, D. João II e D. Manuel I. Embora a maior parte dos acontecimentos mencionados por estes anais sejam também conhecidos através de outras fontes históricas, alguns transmitem diversos acontecimentos não mencionados noutros locais, sendo, por isso, especialmente relevantes. Um exemplo interessante é a cerimónia de investidura do infante D. Fernando, irmão de D. Afonso V e pai de D. Manuel, ocorrida em Lisboa a 10 de agosto de 1456, a qual é descrita, com certo detalhe, em alguns destes anais (segundo já foi comentado por Aguiar 2018). Também não é fácil perceber-se a génese destes textos. Alguns parecem resultar da compilação e/ou continuação de textos analísticos prévios (várias entradas repetem-se, ipsis verbis ou quase); outros, terão sido redigidos e acrescentados à medida que os acontecimentos históricos dignos de registo se iam sucedendo. É também notória a relação destes textos com o género historiográfico por excelência desta época, as crónicas. Com efeito, dos 21 textos atualmente elencados em BITAGAP, 6 estão copiados em manuscritos (ou, no caso do BITAGAP texid 11379, num impresso) que contêm, também, cópias ou sumários de crónicas, especialmente as de Rui de Pina e de Duarte Galvão. Esta circunstância já indicia uma proximidade entre ambos estes géneros, mas uma observação mais atenta poderá estreitá-la ainda mais. Com efeito, existem manuscritos do século XVI que contêm textos formalmente analísticos mas que, segundo explicitam, resultam da abreviação do conteúdo de crónicas (especialmente as de Fernão Lopes, Rui de Pina e Duarte Galvão), constituindo, assim, o que poderá ser apelidado de “sumários analísticos” (um exemplo, já editado, é Costa 1996). Este facto, junto com a evidente proximidade destes textos com as crónicas, seja do ponto de vista material, seja do conteúdo, leva a pensar que alguns dos textos do corpus analístico estabelecido pela BITAGAP podem resultar, também, deste processo, ainda que o não digam. Mas pode também acontecer o contrário, isto é, que alguns destes anais tenham sido fonte das crónicas. Só um estudo aprofundado, que tenha em conta quer a tradição manuscrita dos anais, quer a das crónicas, permitirá afirmar uma destas (ou ambas estas) hipóteses. Estes anais em língua portuguesa serão editados, com notas, introduções e comentários que os contextualizem, numa coleção de textos antigos dedicados à figura de D. Afonso Henriques, em fase de preparação, e serão também tidos em conta pelo projeto Aranhis, que procura integrar os anais portugueses (em português e em latim) com os anais ibéricos.
Vejamos, entretanto, alguns dos anais descobertos pela BITAGAP, e algumas das suas caraterísticas.
Um dos textos mais interessantes, e digno de ponderado estudo (que está a fazer-se) é o BITAGAP texid 18130, convencionalmente apelidado (quase todos os títulos deste corpus são convencionais) de “Descrição do mundo e notícias analísticas”. Trata-se de uma extensa compilação analística, das mais extensas do corpus (só comparável em extensão ao conhecido Livro da Noa–BITAGAP texid 1057–e à chamada Iª Crónica Breve de Santa Cruz de Coimbra–BITAGAP texid 1240). Ocupa 24 fólios na única cópia conhecida, o manuscrito 51-X-22 da Biblioteca da Ajuda (BITAGAP manid 3984), das primeiras décadas do século XVI. É um dos exemplos de associação dos anais às crónicas, pois esse manuscrito inclui, entre outros textos, uma cópia da Crónica de D. João II de Rui de Pina, com notáveis variantes (incluindo o prólogo, que não é de Rui de Pina, mas, possivelmente, do compilador deste manuscrito). Esta compilação analística tem a introduzi-la, e a contextualizá-la, uma descrição do mundo limitada à Europa, Ásia e África (o que estará indicando a sua possível antiguidade) e uma contagem das famosas sete idades do mundo (fólios 111-112, segundo a numeração moderna, que se sobrepôs a uma anterior e não coincidente). A compilação analística propriamente dita segue, grosso modo, uma ordem cronológica, começando pelo nascimento de Alexandre Magno e prosseguindo com diversos acontecimentos da história universal e, sobretudo, peninsular, antes de entrar a tratar do reinado de D. Afonso Henriques, momento a partir do qual as entradas se ocupam de acontecimentos dos sucessivos reinados portugueses, até ao ano de 1525.

A parte inicial desta compilação analística tem evidentes pontos de contacto e mesmo entradas em comum com a chamada Iª Crónica Breve de Santa Cruz de Coimbra e com anais castelhanos, o que revela tratar-se de uma compilação pelo menos parcialmente baseada em textos bem mais antigos. A maior parte (a partir do fólio 115r) desta compilação é, porém, ocupada com acontecimentos do reinado de D. João I e seguintes (e especialmente dos reinados de D. Afonso V, D. João II e D. Manuel), com algumas entradas referentes a acontecimentos não conhecidos de outras fontes narrativas.

Outro exemplo de associação às crónicas e de uma compilação analística extensa é o conjunto de anais (BITAGAP texid 34129) copiado no ms. Casa Fronteira e Alorna, número 5, da Torre do Tombo (BITAGAP manid 1398). Trata-se de um manuscrito também da primeira metade do século XVI que contém um conjunto de cópias das crónicas de Duarte Galvão e de Rui de Pina (até à de Afonso IV), curiosas porque, frequentemente, copiam apenas o início e o final dos capítulos, originando, as mais das vezes, texto sem sentido. Após a Crónica de D. Afonso IV, surge esta compilação analística, que ocupa os fólios 271v-278v, a qual começa com a batalha do Salado (1340) e termina com a morte da rainha D. Maria, em 1517. Várias entradas são comuns a outros anais e muitas são especialmente dedicadas ao reinado de D. João II, também aqui com acontecimentos nem sempre conhecidos por outras fontes narrativas.

Um terceiro caso interessante é o do texto intitulado “Memoriall dallgũas cousas” (BITAGAP texid 18624), na cópia mais antiga conhecida (COD. 13182 da BNP, BITAGAP manid 1346), uma cópia muito cuidada, com epígrafes a vermelho separando cada uma das entradas. Mais uma vez, estamos perante um conjunto analístico que faz parte de uma miscelânea manuscrita que contém a cópia de uma crónica, neste caso a Crónica de D. Afonso Henriques de Duarte Galvão, entre outros textos (entre os quais uma versão [BITAGAP texid 10498] da célebre Lenda de Gaia já editada e estudada por Ramos 2004). Este conjunto começa com a batalha de Aljubarrota (1385) e termina com o surto de peste de 1520, sendo a maior parte das entradas (algumas extensas e nem todas seguindo a ordem cronológica) dos reinados de D. Afonso V, D. João II e D. Manuel. Uma particularidade interessante deste manuscrito é a sua proveniência, pois, segundo apurou Ramos 2004, a sua origem está, muito provavelmente, numa comunidade religiosa feminina de Guimarães–o que mostra a circulação alargada deste tipo de miscelâneas, incluindo os textos analísticos nelas copiadas. Desta vez, conhece-se uma outra cópia deste texto, mais tardia (século XVII), com variantes e intitulada “Lembranças antiguas”, no manuscrito 2436 da BNE (BITAGAP manid 5253), fólios 228r a 237r. A entrada mais recente desta cópia é, porém, do ano de 1508, o que, em conjunto com as variantes, levanta o problema de tratar-se, ou não, de uma cópia modificada do manuscrito quinhentista de Guimarães.

Um último caso pode ser relevado, porque, contrariamente aos anteriores, não faz parte de compilações historiográficas, mas sim de uma cópia de documentos. Trata-se de um breve conjunto analístico copiado no fólio 180v do Livro 517 da Alfândega de Vila do Conde, Torre do Tombo (BITAGAP manid 6896), por isso designados como “Anais de Vila do Conde” (BITAGAP texid 25247). Começa, uma vez mais, com a batalha do Salado, e termina com a vinda do duque de Lencastre à Península Ibérica, no contexto das lutas pela sucessão dos tronos de Portugal e de Castela, no final do século XIV. Antecede estes anais uma lista dos cavaleiros portugueses que estiveram presentes na conquista de Ceuta (1415), mas, de facto, a maior parte deste manuscrito é de documentos relacionados com a atividade da alfândega de Vila do Conde, nos séculos XV e XVI. É interessante, por isso (e relevante), a presença de anais num manuscrito deste tipo.
Referências
Aguiar, Miguel (2018). Cavaleiros e Cavalaria. Ideologia, práticas e rituais aristocráticos em Portugal nos Séculos XIV e XV. Porto: Teodolito.
Bautista, Francisco (2009). “Breve historiografía: listas regias y Anales en la Peninsula Iberica (Siglos VII-XII)”. Talia Dixit. Núm. 4, pp. 113-90: https://publicaciones.unex.es/index.php/TD/article/view/213
Costa, José Pereira da, ed. (1996). Crónicas dos Reis de Portugal e Sumários das suas vidas: D. Pedro I, D. Fernando, D. João I, D. Duarte, D. Afonso V, D. João II / Gaspar Correia. Lisboa: Academia das Ciências.
David, Pierre (1947). Études Historiques sur la Galice et le Portugal du VI au XII siécle. Paris: Institut Français au Portugal.
Furtado, Rodrigo (2021). “Writing history in Portugal before 1200”. Journal of Medieval History. Vol. 47, Issue 2, pp. 145-73: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/03044181.2021.1902375
Ramos, Maria Ana (2004). “Hestorja dell Rej dom Ramjro de lleom”…. Nova versão de “A Lenda de Gaia”. Critica del Testo. Romània romana. Giornata di studi in onore di Giuseppe Tavani. Vol. 7 n. 2, pp. 791-843.
Sharrer, Harvey L. (2022). “BITAGAP (Bibliografia de Textos Antigos Galegos e Portugueses): um armazém da memória histórica” in R. Pichel (ed.), Tenh’eu que mi fez el i mui gran ben. Estudos sobre cultura escrita medieval dedicados a Harvey L. Sharrer. Madrid: Sílex, pp. 39-67.
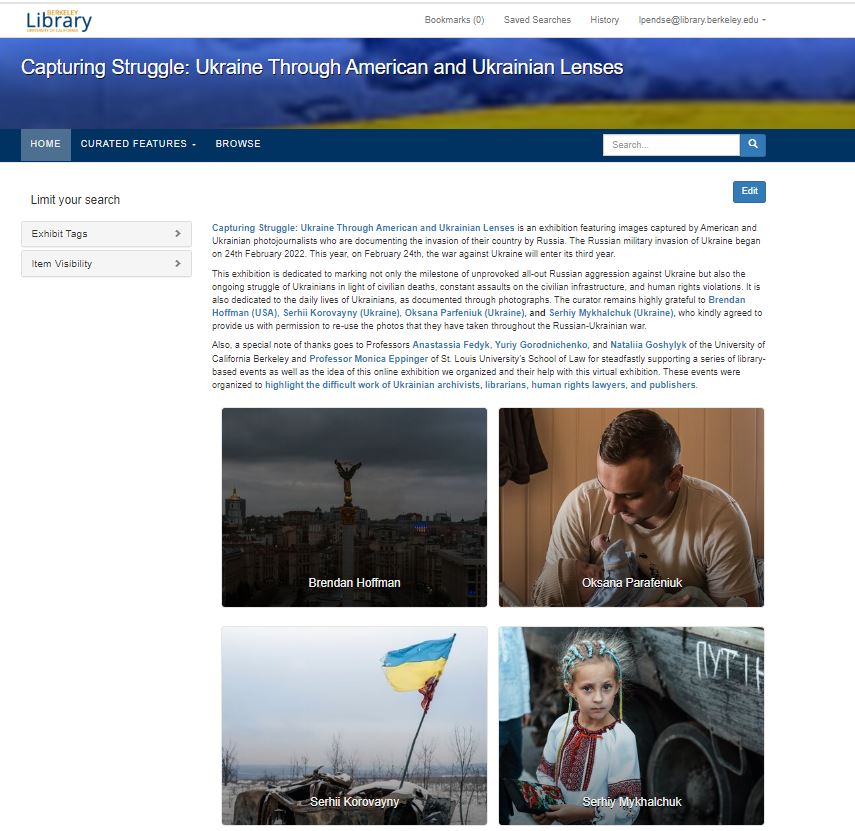
UC Berkeley Library’s Online Exhibition: Capturing Struggle: Ukraine Through American and Ukrainian Lenses
The exhibition not only commemorates the unprovoked Russian aggression but also sheds light on the ongoing struggle of Ukrainians amidst civilian deaths, assaults on infrastructure, and human rights violations. It offers a glimpse into the daily lives of Ukrainians through compelling photographs. We are grateful to Brendan Hoffman (USA), Serhii Korovayny, Oksana Parfeniuk, and Serhiy Mykhalchuk (Ukraine) for generously allowing us to showcase their impactful work. Also, We want to thank Svidok and AI for Good Foundation for helping us with additional photos.
Special thanks to Professors Anastassia Fedyk, Yuriy Gorodnichenko, and Nataliia Goshylyk of the University of California Berkeley, and Professor Monica Eppinger of St. Louis University’s School of Law for their unwavering support in organizing this online exhibition and related events. These events aim to highlight the resilience of Ukrainian archivists, librarians, human rights lawyers, and publishers. We also have featured recommended readings from UC Berkeley Library’s collections based on the faculty input (In English, In Ukrainian).
The idea for bringing this exhibition to the library originated at Fulbright Ukraine and Institute of International Education Kyiv, of which the Director of both these institutions, Dr. Jessica Zychowicz, is a UC Berkeley Alumna (English, ’04). Deputy Director Inna Barysh, Communications Officer Marian Luniv, and Program Officer Mariia Kravchenko envisioned the first exhibit which took place in Vynnitsia, Ukraine, and continue to co-curate all iterations. The photographs provided by Serhii Korovayny and Serihy M. were not part of the original Fullbright exhibition and were a later curatorial addition. Fulbright Ukraine has held exhibitions at several U.S. and European universities and museums, including in locations in Berlin, Czech Republic, and Bulgaria attended by U.S. Ambassadors.
Explore the exhibition here: Capturing Struggle: Ukraine Through American and Ukrainian Lenses.
Exploring the Arts during Black History Month
“The A&AePortal is committed to featuring groundbreaking and authoritative books on African Americans and the arts. Here are some highlights—see what might be helpful in your teaching, coursework, or research!” – from the A&Ae Portal Website.
Explore the Arts and Architecture E Portal from Yale University Press provided to you by UC Berkeley Library. Click the link to see these and other titles about the African American and Black Diaspora.
Visit the Art History/ Classics library to view more new books on Black and African American Artists now on display in 308 Doe.