Tag: USSR
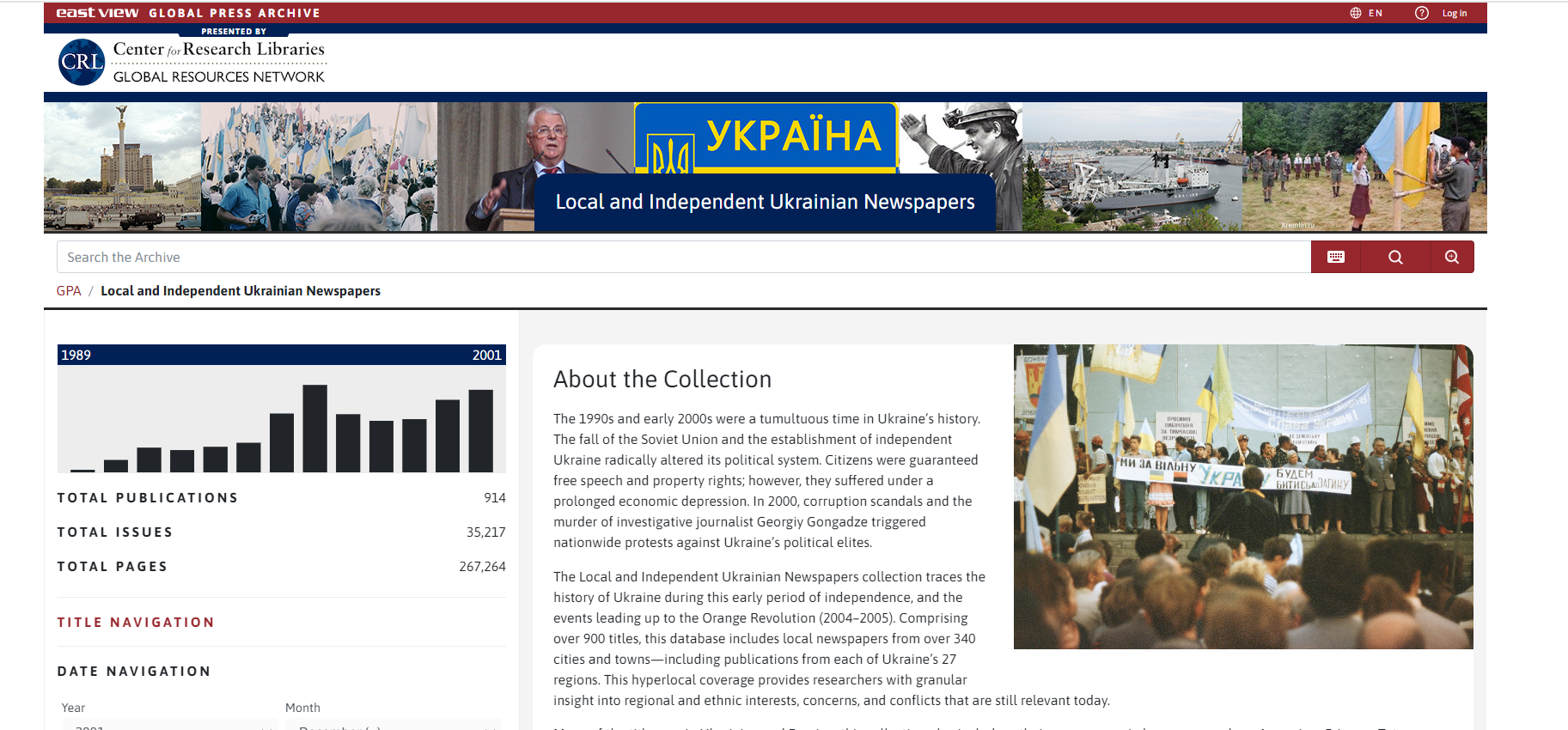
Local and Independent Ukrainian Newspapers on Global Press Archive Electronically Available
The 1990s and early 2000s marked a turbulent period in Ukraine’s history due to the fall of the Soviet Union and the emergence of an independent Ukraine. Despite gaining free speech and property rights, citizens faced economic hardships. Corruption scandals and the murder of journalist Georgiy Gongadze in 2000 sparked nationwide protests against the political elite. The Local and Independent Ukrainian Newspapers collection covers this era up to the Orange Revolution (2004–2005), offering insights from over 900 newspapers across 340 cities, reflecting regional and ethnic dynamics. The collection includes publications in Ukrainian, Russian, and other languages like Armenian, German, Polish, etc., providing a detailed view of historical events. Access to this database is supported by the Center for Research Libraries and its members.
One can access this collection here.
New Digital Resource: Собрание законов и распоряжений правительства РСФСР и СССР= Collection of laws and orders of the government of the RSFSR and the USSR
Recently in light of Russian invasion of Ukraine, with almost everything Russian being canceled in society at large, I wanted to bring to our readers’ attention a new digital resource on the Collection of laws and orders of the government of the RSFSR and the USSR. The resource is in Russian, and it was created by the Elektronnaia biblioteka istoricheskikh dokumentov (Электронная библиотека исторических документов).
The source provides access to digital copies of the laws and various orders of the Russian Soviet Socialist Republic and Soviet Union. I hope historians of the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation will find this resource of academic interest.
One can search within the text using specific keywords.

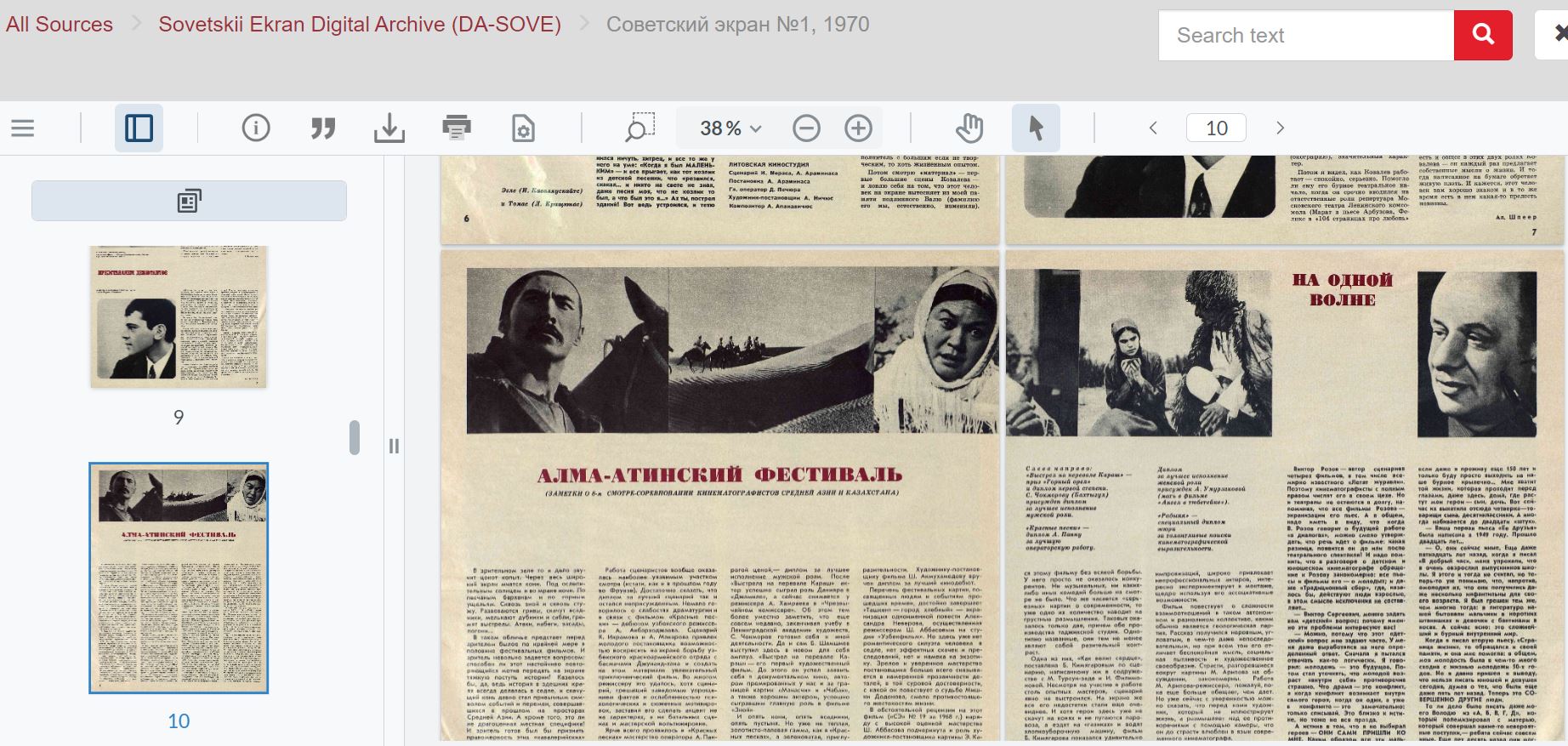
Sovetskii Ekran (Soviet Film) Digital Archive at UC Berkeley Library
The Library has purchased the Digital Archive of a Soviet film magazine: Sovetskii Ekran. The archive provides access to the full-text of journal issues that were published from 1925-1998.
Below is the screenshot of the landing page of the Sovietskii Ekran.

At the time of writing this blog, the digitization of issues was completed through 1970 and the additional digitization was in progress.
About the journal:
Soviet Screen was a magazine in the USSR that ran from 1925 to 1998 (with a break from 1941 to 1957). It talked about movies, both from the Soviet Union and other countries, cinema history, and had articles critiquing films. They also had reader polls each year to pick the best film, actor, actress, film for children, and music film.
The magazine had different names over the years, like Screen Film Gazeta in 1925, Cinema and Life in 1929–1930, Proletarian Cinema from 1931–1939, and Screen from 1991–1997. Before 1992, it was connected to the Union of Cinematographers of the USSR State Committee for Cinematography and the USSR.
In 1984, they printed 1.9 million copies. In 1991, the editor was Victor Dyomin, and the magazine was published under the title: Screen. It started coming out less often, monthly instead of more frequently. It kept going as Screen Magazine until 1997, then for a few months in 1997-1998, it went back to its old name-Soviet Screen. But it couldn’t survive the financial troubles in 1998 and had to stop publishing (Source: Wikip.).
Primary sources: Russian language historical ebook collections
This post highlights some of the Library’s acquisitions of Russian-language historical ebook collections that may have escaped your notice.
 Soviet Anti-Religious Propaganda ebook collection
Soviet Anti-Religious Propaganda ebook collection
East View has digitized a collection of 280 e-books that are most emblematic of Soviet anti-religious fervor. They were published mainly in the 1920s and 1930s on a variety of atheist or anti-religious topics, with titles including Christianity versus Communism, Church versus Democracy, and The Trial of God.
Another collection from East View of 116 ebooks, originally published from 1928 to 1948, relating to the golden age of Soviet Cinema.
An ebook collection of 778 works from Brill Online. It represents works of all Russian literary avant-garde schools, most published betwen 1910-1940. According to the publisher, “the strength of this collection is in its sheer range. It contains many rare and intriguingly obscure books, as well as well-known and critically acclaimed texts, almanacs, periodicals, literary manifests. This makes it a gold mine for art historians and literary scholars alike. Represented in it are more than 30 literary groups without which the history of twentieth-century Russian literature would have been very different. Among the groups included are the Ego-Futurists and Cubo-Futurists, the Imaginists, the Constructivists, the Biocosmists, and the infamous nichevoki – who, in their most radical manifestoes, professed complete abstinence from literary creation.”
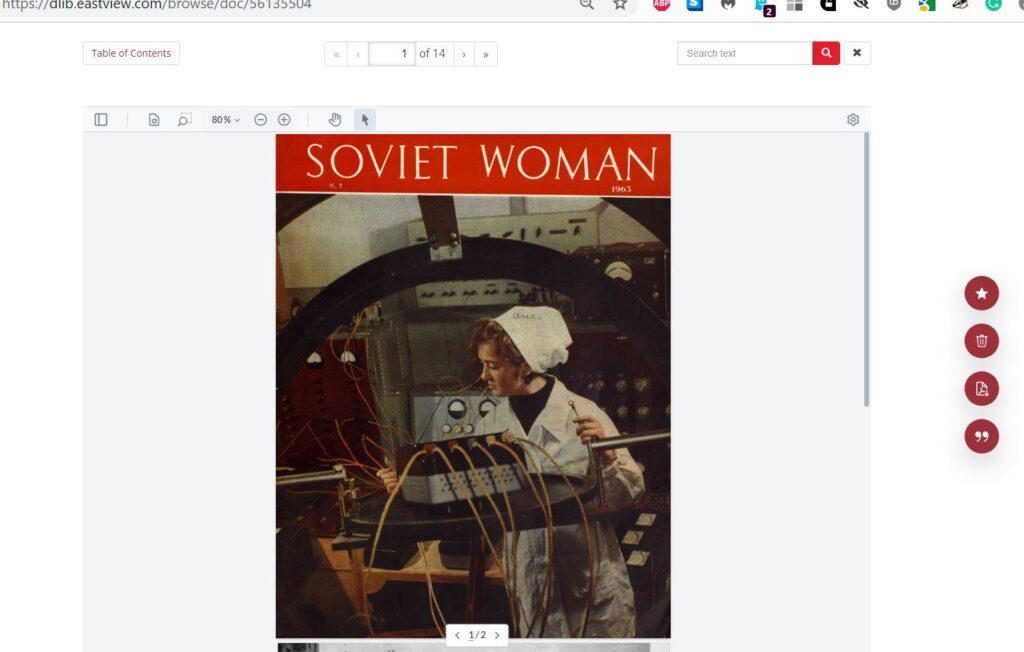
Library Trial of Soviet Woman Digital Archive (25 October 2021 through 24 November 2021).
We have set up a thirty-day trial of the Soviet Woman Digital Archive (1945-1991)
To link to this database during the trial is below:
Published initially under the aegis of the Soviet Women’s Anti-Fascist Committee and the Central Council of Trade Unions of the USSR, in the aftermath of WWII in 1945, the Soviet Woman magazine began as a bi-monthly illustrated magazine tasked with countering anti-Soviet propaganda. The magazine introduced Western audiences to the lifestyle of Soviet women, their role in the post-WWII rebuilding of the Soviet economy, and praised their achievements in the arts and the sciences.
Additional Information:
The magazine covered issues dealing with economics, politics, life abroad, life in Soviet republics, women’s fashion, as well as broader issues in culture and the arts. One of its most popular features was the translations of Soviet literary works, making available in English, (and other languages) works of Russian and Soviet writers that were previously unavailable. An important communist propaganda outlet, the magazine continued its run until the collapse of the USSR in 1991.
Coverage:1945-1991
Vendor: East View
Producer:Правда
Happy International Women’s Day-March 8th!
Today, March 8, is celebrated around the world as International Women’s Day. In the USSR, this holiday was celebrated rather religiously as the role of Soviet women in the success of the Soviet experiment and internationalist policies was undeniable. The conceptualization of the Soviet Woman as an idea was nuanced and complicated. A Wikipedia entry starts as follows, “International Women’s Day (IWD) is a global holiday celebrated annually on March 8 to commemorate the cultural, political, and socioeconomic achievements of women.[3] It is also a focal point in the women’s rights movement, bringing attention to issues such as gender equality, reproductive rights, and violence against women.”[4]
 Image Source: Messy Nessy (https://www.messynessychic.com/2017/03/10/the-soviet-communist-origins-of-international-womens-day/) Fair Academic Use Only. The copyright belongs to the creator of the image.
Image Source: Messy Nessy (https://www.messynessychic.com/2017/03/10/the-soviet-communist-origins-of-international-womens-day/) Fair Academic Use Only. The copyright belongs to the creator of the image.
Temma Kaplan’s article, “On the Socialist Origins of International Women’s Day,” provides insights into how this day became a signifier in the Socialist World. One however forgets that the origins of this day can be found in Germany as noted by Rochelle Goldberg Ruthchild in her article, “From West to East International Women’s Day, the First Decade.” Here you can access some materials from UC Berkeley Library’s catalog regarding International Women’s Day. Also, some posters from the collections of several California libraries can be found here.
One can watch an interesting clip from YouTube with a title, “Демонстрация женщин в 1917 году. Московские Новости. 8 марта 1967,” and a concert honoring women in the Soviet Union from 1984.
Below is the clip of a 1963 concert dedicated to International Women’s day:Концерт 8 Марта из Большого театра СССР (1963).
And here is a clip of protest on the occasion of March 8th from Mexico.