Tag: Caribbean Studies
Trial of Brill’s Revolución y Cultura, 1961–2003 (ending February 21, 2023)
Revolución y Cultura, 1961–2003(Cuba)
Please access the trial through February 21, 2023, here
At UC Berkeley Library, we have several individual issues of Revolución y Cultura, however, Brill has produced a complete digitized archive of it that is searchable. We have set up a trial of this resource through February 21, 2023. We look forward to hearing your comments regarding the utility of this resource in your teaching and research. Please feel free to contact your librarian for the Caribbean and Latin American Studies here.
About:
Revolución y Cultura is a fundamental and often unique resource for the study of more than half a century of Cuban culture. Founded as a biweekly in 1961 under the title Pueblo y Cultura and continued in 1965 as the bilingual magazine Revolution et/and Culture and as RC in 1967, Revolución y Cultura has published uninterruptedly since March 1972. From its foundation until 1977, when the Cuban Ministry of Culture was created, it appeared as the official organ of Cuba’s National Council of Culture.
From 2004 to 2019 it was published both in print and electronically. Since mid-2019, Revolución y Cultura is published online only. Revolución y Cultura is listed in the UNESCO Portal of Culture of Latin America and the Caribbean (Source: Brill)
Cuba: Grito de Yara (10 October 1868)
Each year, on 10th October, the Cubans all over the world commemorate the call for national independence. The “Grito de Yara,” is one of many important events in the complex historical trajectory of Cuba that unleashed the potential of the national consciousness through rebellions against the Spanish imperial authorities. The full text of the “Manifiesto de la Junta Revolucionaria de la Isla de Cuba” can be read by clicking on the link here.
At UC Berkeley Library, despite our West Coast location and our Pacific Rim orientation, we have a large collection of books that will enlighten our readers about what does “Grito de Yara” means. The other essential Open Access source is dLOC (Digital Library of the Caribbean) where one can browse documents related to the “Grito de Yara.“
Below are some titles that might of interest to the readers of this blog. Since we believe in the equitable access, I am providing some links to the full-text of these items.
Below is a clip from a film,
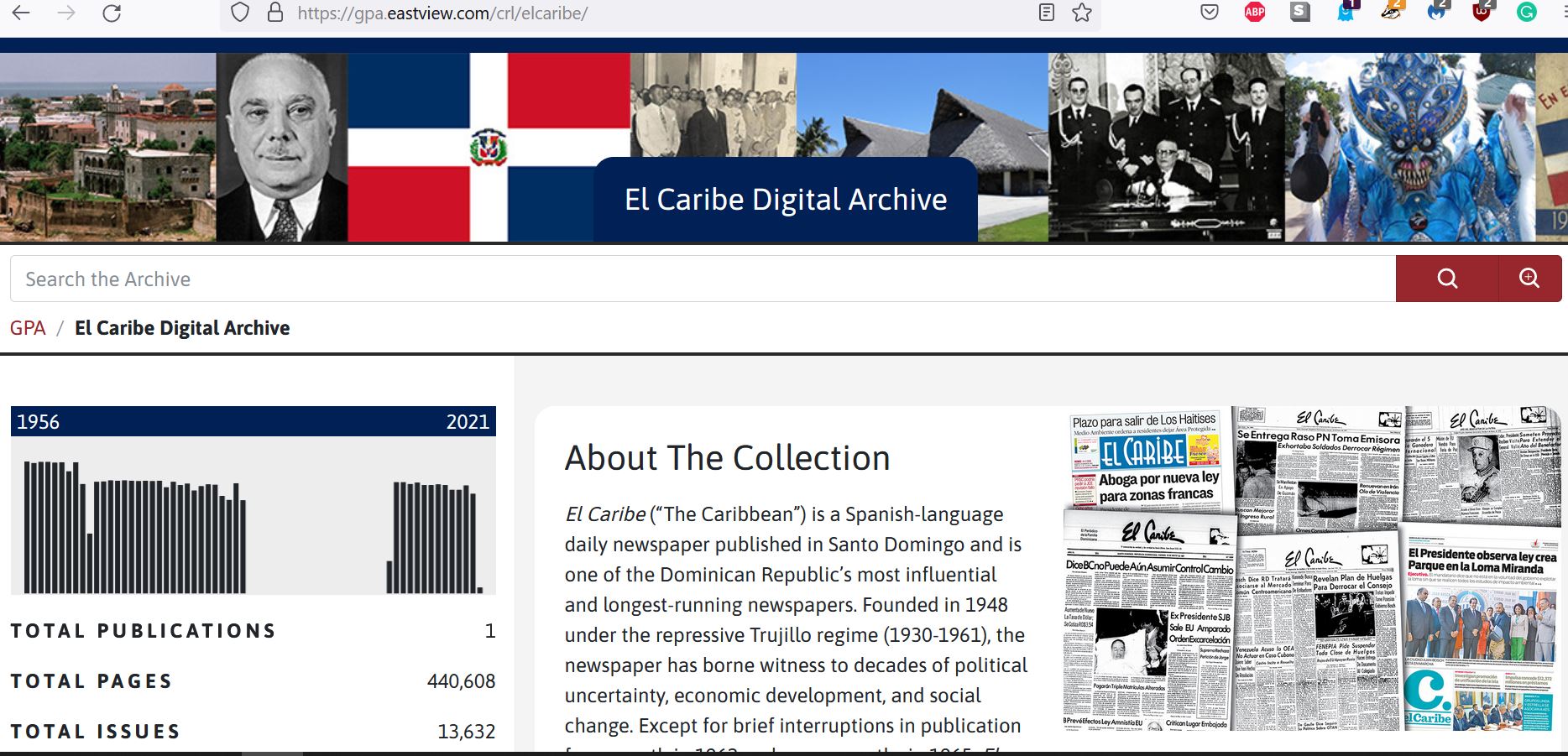
El Caribe Digital Archive-CRL Global Press Alliance
CRL recently announced a launch of a new digital archive on its Global Press Alliance Archive of El Caribe Newspaper. The site’s self-description is as follows, “El Caribe (“The Caribbean”) is a Spanish-language daily newspaper published in Santo Domingo and is one of the Dominican Republic’s most influential and longest-running newspapers. Founded in 1948 under the repressive Trujillo regime (1930-1961), the newspaper has borne witness to decades of political uncertainty, economic development, and social change. Except for brief interruptions in publication for a month in 1962 and seven months in 1965, El Caribe has been a constant chronicle of national and international news, both for the Dominican Republic and the broader Caribbean region.”
Since the newspaper is still in copyright, UC Berkeley users have to authenticate using their institutional login. For more information see here: https://www.lib.berkeley.edu/using-the-libraries/connect-off-campus